Quick Start
Authentication is the process of verifying that a user is who he or she claims to be. It answers the question Who is the user?.
Example: a user enters their login credentials to connect to the application.
Authorization, also known as Access Control, is the process of determining what an authenticated user is allowed to do. It answers the question Does the user has the right to do what they ask?.
Example: a user tries to access the administrator page.
This document focuses on explaining how authentication works in FoalTS and gives several code examples to get started quickly. Further explanations are given in other pages of the documentation.
The Basics
The strength of FoalTS authentication system is that it can be used in a wide variety of applications. Whether you want to build a stateless REST API that uses social ID tokens or a traditional web application with templates, cookies and redirects, FoalTS provides you with the tools to do so. You can choose the elements you need and build your own authentication process.
| Auth Support | |
|---|---|
| Kind of Application | API, Regular Web App, SPA+API, Mobile+API |
| State management | Stateful (Session Tokens), Stateless (JSON Web Tokens) |
| Credentials | Passwords, Social |
| Token storage | Cookies, localStorage, Mobile, etc |
Whatever architecture you choose, the authentication process will always follow the same pattern.
Step 1: the user logs in.
In some architectures, this step might be delegated to an external service: Google, Cognito, Auth0, etc
- Verify the credentials (email & password, username & password, social, etc).
- Generate a token (stateless or stateful).
- Return the token to the client (in a cookie, in the response body or in a header).
Step 2: once logged in, the user keeps being authenticated on subsequent requests.
- On each request, receive and check the token and retrieve the associated user if the token is valid.
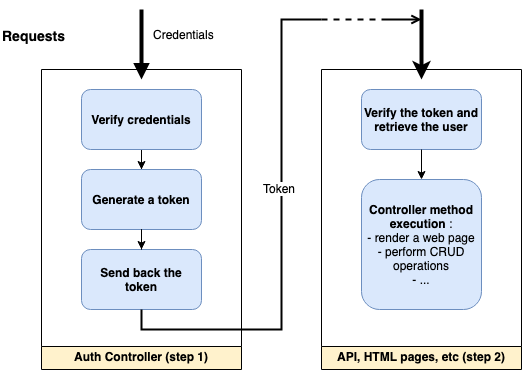
The Available Tokens (step 1)
FoalTS provides two ways to generate tokens:
- Session Tokens (stateful): They are probably the easiest way to manage authentication with Foal. Creation is straightforward, expiration is managed automatically and revocation is easy. Using session tokens keeps your code concise and does not require additional knowledge.
Unlike other restrictive session management systems, FoalTS sessions are not limited to traditional applications that use cookies, redirection and server-side rendering. You can choose to use sessions without cookies, in a SPA+API or Mobile+API architecture and deploy your application to a serverless environment.
- JSON Web Tokens (stateless): For more advanced developers, JWTs can be used to create stateless authentication or authentication that works with external social providers.
The Authentication Hooks (step 2)
In step 2, the hooks TokenRequired and TokenOptional take care of checking the session tokens and retrieve their associated user. The same applies to JWTRequired and JWTOptional with JSON Web Tokens.
You will find more information in the documentation pages dedicated to them.
Code Examples
The four examples below can be used directly in your application to configure login, logout and signup routes. You can use them as they are or customize them to meet your specific needs.
For these examples, we will use TypeORM as default ORM and emails and passwords as credentials. An API will allow authenticated users to list products with the request GET /api/products.
src/app/app.controller.ts
import { controller } from '@foal/core';
export class AppController {
subControllers = [
AuthController,
controller('/api', ApiController),
];
}
src/app/entities/user.entity.ts
@Entity()
export class User {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@Column({ unique: true })
email: string;
@Column()
password: string;
}
SPA + API / Mobile + API (no cookies)
With these implementations, the user logs in with the route POST /login and receives a token in exchange in the response body. Then, when the user makes a request to the API, the token must be included in the Authorization header using the bearer sheme.
Authorization: Bearer my-token
You may need to enable CORS or use Frontend Integration to get this example work with an SPA.
Sessions Tokens
First generate a secret:
foal createsecret
And save this secret in a .env file:
SETTINGS_SESSION_SECRET=my-secret
src/app/controllers/auth.controller.ts
import { dependency, Get, Post, Session, TokenRequired, ValidateBody } from '@foal/core';
import { TypeORMStore } from '@foal/typeorm';
// ... to complete
const credentialsSchema = {
additionalProperties: false,
properties: {
email: { type: 'string', format: 'email' },
password: { type: 'string' }
},
required: [ 'email', 'password' ],
type: 'object',
};
export class AuthController {
@dependency
store: TypeORMStore;
@Post('/signup')
@ValidateBody(credentialsSchema)
async signup(ctx: Context) {
const user = new User();
user.email = ctx.request.body.email;
user.password = await hashPassword(ctx.request.body.password);
await getRepository(User).save(user);
const session = await this.store.createAndSaveSessionFromUser(user);
return new HttpResponseOK({
token: session.getToken()
});
}
@Post('/login')
@ValidateBody(credentialsSchema)
async login(ctx: Context) {
const user = await getRepository(User).findOne({ email: ctx.request.body.email });
if (!user) {
return new HttpResponseUnauthorized();
}
if (!await verifyPassword(ctx.request.body.password, user.password)) {
return new HttpResponseUnauthorized();
}
const session = await this.store.createAndSaveSessionFromUser(user);
return new HttpResponseOK({
token: session.getToken()
});
}
@Post('/logout')
@TokenRequired({ store: TypeORMStore, extendLifeTimeOrUpdate: false })
async logout(ctx: Context<any, Session>) {
await this.store.destroy(ctx.session.sessionID);
return new HttpResponseNoContent();
}
}
src/app/controllers/api.controller.ts
@TokenRequired({ store: TypeORMStore })
export class ApiController {
@Get('/products')
readProducts() {
return new HttpResponseOK([]);
}
}
JSON Web Tokens
First generate a secret:
foal createsecret
And save this secret in a .env file:
SETTINGS_JWT_SECRET_OR_PUBLIC_KEY=my-secret
src/app/controllers/auth.controller.ts
const credentialsSchema = {
additionalProperties: false,
properties: {
email: { type: 'string', format: 'email' },
password: { type: 'string' }
},
required: [ 'email', 'password' ],
type: 'object',
};
export class AuthController {
@Post('/signup')
@ValidateBody(credentialsSchema)
async signup(ctx: Context) {
const user = new User();
user.email = ctx.request.body.email;
user.password = await hashPassword(ctx.request.body.password);
await getRepository(User).save(user);
return this.generateLoginResponse(user);
}
@Post('/login')
@ValidateBody(credentialsSchema)
async login(ctx: Context) {
const user = await getRepository(User).findOne({ email: ctx.request.body.email });
if (!user) {
return new HttpResponseUnauthorized();
}
if (!await verifyPassword(ctx.request.body.password, user.password)) {
return new HttpResponseUnauthorized();
}
return this.generateLoginResponse(user);
}
private async generateLoginResponse(user: User): Promise<HttpResponseOK> {
const payload = {
email: user.email,
id: user.id,
};
const secret = Config.get<string>('settings.jwt.secretOrPublicKey');
const token = await new Promise<string>((resolve, reject) => {
sign(payload, secret, { subject: user.id.toString() }, (err, value: string) => {
if (err) {
return reject(err);
}
resolve(value);
});
});
return new HttpResponseOK({
token
});
}
}
src/app/controllers/api.controller.ts
@JWTRequired()
export class ApiController {
@Get('/products')
readProducts() {
return new HttpResponseOK([]);
}
}
SPA + API (with cookies)
As you use cookies, you must add a CSRF protection to your application.
In this implementation, the authentication is managed with cookies.
You may need to enable CORS or use Frontend Integration to get this example work with an SPA.
Session Tokens
First generate a secret:
foal createsecret
And save this secret in a .env file:
SETTINGS_SESSION_SECRET=my-secret
src/app/controllers/auth.controller.ts
const credentialsSchema = {
additionalProperties: false,
properties: {
email: { type: 'string', format: 'email' },
password: { type: 'string' }
},
required: [ 'email', 'password' ],
type: 'object',
};
export class AuthController {
@dependency
store: TypeORMStore;
@Post('/signup')
@ValidateBody(credentialsSchema)
async signup(ctx: Context) {
const user = new User();
user.email = ctx.request.body.email;
user.password = await hashPassword(ctx.request.body.password);
await getRepository(User).save(user);
const session = await this.store.createAndSaveSessionFromUser(user);
const response = new HttpResponseNoContent();
const token = session.getToken();
setSessionCookie(response, token);
return response;
}
@Post('/login')
@ValidateBody(credentialsSchema)
async login(ctx: Context) {
const user = await getRepository(User).findOne({ email: ctx.request.body.email });
if (!user) {
return new HttpResponseUnauthorized();
}
if (!await verifyPassword(ctx.request.body.password, user.password)) {
return new HttpResponseUnauthorized();
}
const session = await this.store.createAndSaveSessionFromUser(user);
const response = new HttpResponseNoContent();
const token = session.getToken();
setSessionCookie(response, token);
return response;
}
@Post('/logout')
@TokenRequired({
cookie: true,
extendLifeTimeOrUpdate: false,
store: TypeORMStore,
})
async logout(ctx: Context<any, Session>) {
await this.store.destroy(ctx.session.sessionID);
const response = new HttpResponseNoContent();
removeSessionCookie(response);
return response;
}
}
src/app/controllers/api.controller.ts
@TokenRequired({ store: TypeORMStore, cookie: true })
export class ApiController {
@Get('/products')
readProducts() {
return new HttpResponseOK([]);
}
}
Regular Web Applications (with cookies and redirections)
As you use cookies, you must add a CSRF protection to your application.
In this implementation, the authentication is managed with cookies and redirections.
First generate a secret:
foal createsecret
And save this secret in a .env file:
SETTINGS_SESSION_SECRET=my-secret
src/app/app.controller.ts
import { controller } from '@foal/core';
export class AppController {
subControllers = [
AuthController,
ViewController,
controller('/api', ApiController),
];
}
src/app/controllers/auth.controller.ts
const credentialsSchema = {
additionalProperties: false,
properties: {
email: { type: 'string', format: 'email' },
password: { type: 'string' }
},
required: [ 'email', 'password' ],
type: 'object',
};
export class AuthController {
@dependency
store: TypeORMStore;
@Post('/signup')
@ValidateBody(credentialsSchema)
async signup(ctx: Context) {
const user = new User();
user.email = ctx.request.body.email;
user.password = await hashPassword(ctx.request.body.password);
await getRepository(User).save(user);
const session = await this.store.createAndSaveSessionFromUser(user);
const response = new HttpResponseRedirect('/home');
const token = session.getToken();
setSessionCookie(response, token);
return response;
}
@Post('/login')
@ValidateBody(credentialsSchema)
async login(ctx: Context) {
const user = await getRepository(User).findOne({ email: ctx.request.body.email });
if (!user) {
return new HttpResponseRedirect('/login');
}
if (!await verifyPassword(ctx.request.body.password, user.password)) {
return new HttpResponseRedirect('/login');
}
const session = await this.store.createAndSaveSessionFromUser(user);
const response = new HttpResponseRedirect('/home');
const token = session.getToken();
setSessionCookie(response, token);
return response;
}
@Post('/logout')
@TokenRequired({
cookie: true,
extendLifeTimeOrUpdate: false,
redirectTo: '/login',
store: TypeORMStore,
})
async logout(ctx: Context<any, Session>) {
await this.store.destroy(ctx.session.sessionID);
const response = new HttpResponseRedirect('/login');
removeSessionCookie(response);
return response;
}
}
src/app/controllers/view.controller.ts
export class ViewController {
@Get('/home')
@TokenRequired({ store: TypeORMStore, cookie: true, redirectTo: '/login' })
home() {
return new HttpResponseOK('Home page');
}
}
src/app/controllers/api.controller.ts
@TokenRequired({ store: TypeORMStore, cookie: true })
export class ApiController {
@Get('/products')
readProducts() {
return new HttpResponseOK([]);
}
}