Grupos y Permisos
In advanced applications, access control can be managed through permissions and groups.
A permission gives a user the right to perform a given action (such as accessing a route).
A group brings together a set of users (a user can belong to more than one group).
Permissions can be attached to a user or a group. Attaching a permission to a group is equivalent to attaching the permission to each of its users.
Examples of groups are the "Free", "Pro" and "Enterprise" plans of a SaaS application. Depending of the price paid by the customers, they have access to certain features whose access are managed by permissions.
Permissions
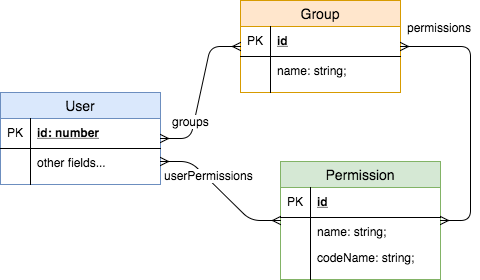
The Permission Entity
| Property name | Type | Database Link |
|---|---|---|
| id | number | Primary auto generated key |
| name | string | |
| codeName | string | Unique, Length: 100 |
Creating Permissions Programmatically
import { Permission } from './src/app/entities';
async function main() {
const perm = new Permission();
perm.codeName = 'secret-perm';
perm.name = 'Permission to access the secret';
await perm.save();
}
Creating Permissions with a Shell Script (CLI)
Create a new script with this command:
foal generate script create-perm
Replace the content of the new created file src/scripts/create-perm.ts with the following:
// 3p
import { Permission } from '@foal/typeorm';
// App
import { dataSource } from '../db';
export const schema = {
additionalProperties: false,
properties: {
codeName: { type: 'string', maxLength: 100 },
name: { type: 'string' },
},
required: [ 'name', 'codeName' ],
type: 'object',
};
export async function main(args: { codeName: string, name: string }) {
const permission = new Permission();
permission.codeName = args.codeName;
permission.name = args.name;
await dataSource.initialize();
try {
console.log(
await permission.save()
);
} catch (error: any) {
console.log(error.message);
} finally {
await dataSource.destroy();
}
}
Then you can create a permission through the command line.
npm run build
foal run create-perm name="Permission to access the secret" codeName="access-secret"
Groups
Groups are used to categorize users. A user can belong to several groups and a group can have several users.
A group can have permissions. They then apply to all its users.
The Group Entity
| Property name | Type | Database Link |
|---|---|---|
| id | number | Primary auto generated key |
| name | string | Length: 80 |
| codeName | string | Unique, Length: 100 |
| permissions | Permission[] | A many-to-many relation with the table permission |
Creating Groups Programmatically
import { Group, Permission } from './src/app/entities';
async function main() {
const perm = new Permission();
perm.codeName = 'delete-users';
perm.name = 'Permission to delete users';
await perm.save();
const group = new Group();
group.codeName = 'admin';
group.name = 'Administrators';
group.permissions = [ perm ];
await group.save();
}
Creating Groups with a Shell Script (CLI)
Create a new script with this command:
foal generate script create-group
Replace the content of the new created file src/scripts/create-group.ts with the following:
// 3p
import { Group, Permission } from '@foal/typeorm';
// App
import { dataSource } from '../db';
export const schema = {
additionalProperties: false,
properties: {
codeName: { type: 'string', maxLength: 100 },
name: { type: 'string', maxLength: 80 },
permissions: { type: 'array', items: { type: 'string' }, uniqueItems: true, default: [] }
},
required: [ 'name', 'codeName' ],
type: 'object',
};
export async function main(args: { codeName: string, name: string, permissions: string[] }) {
const group = new Group();
group.permissions = [];
group.codeName = args.codeName;
group.name = args.name;
await dataSource.initialize();
try {
for (const codeName of args.permissions) {
const permission = await Permission.findOneBy({ codeName });
if (!permission) {
console.log(`No permission with the code name "${codeName}" was found.`);
return;
}
group.permissions.push(permission);
}
console.log(
await group.save()
);
} catch (error: any) {
console.log(error.message);
} finally {
await dataSource.destroy();
}
}
Then you can create a group through the command line.
npm run build
foal run create-perm name="Permission to delete users" codeName="delete-users"
foal run create-group name="Administrators" codeName="admin" permissions="[ \"delete-users\" ]"
Users
The UserWithPermissions Entity
import { UserWithPermissions } from '@foal/typeorm';
import { Entity } from 'typeorm';
@Entity()
export class User extends UserWithPermissions {
}
// You MUST export Group and Permission so that TypeORM can generate migrations.
export { Group, Permission } from '@foal/typeorm';
UserWithPermissions is an abstract class that has useful features to handle access control through permissions and groups. You must extend your User entity from this class to use permissions and groups.
| Property name | Type | Database Link |
|---|---|---|
| id | number | Primary auto generated key |
| groups | Group[] | A many-to-many relation with the table group |
| userPermissions | Permission[] | A many-to-many relation with the table permission |
The hasPerm Method
The hasPerm(permissionCodeName: string) method of the UserWithPermissions class returns true if one of these conditions is true:
- The user has the required permission.
- The user belongs to a group that has the required permission.
The static findOneWithPermissionsBy Method
This method takes an id as parameter and returns the corresponding user with its groups and permissions. If no user is found, the method returns null.
Creating Users with Groups and Permissions with a Shell Script (CLI)
Replace the content of the new created file src/scripts/create-user.ts with the following:
// 3p
import { hashPassword } from '@foal/core';
import { Group, Permission } from '@foal/typeorm';
// App
import { User } from '../app/entities';
import { dataSource } from '../db';
export const schema = {
additionalProperties: false,
properties: {
email: { type: 'string', format: 'email' },
groups: { type: 'array', items: { type: 'string' }, uniqueItems: true, default: [] },
password: { type: 'string' },
userPermissions: { type: 'array', items: { type: 'string' }, uniqueItems: true, default: [] },
},
required: [ 'email', 'password' ],
type: 'object',
};
export async function main(args) {
const user = new User();
user.userPermissions = [];
user.groups = [];
user.email = args.email;
user.password = await hashPassword(args.password);
await dataSource.initialize();
for (const codeName of args.userPermissions as string[]) {
const permission = await Permission.findOneBy({ codeName });
if (!permission) {
console.log(`No permission with the code name "${codeName}" was found.`);
return;
}
user.userPermissions.push(permission);
}
for (const codeName of args.groups as string[]) {
const group = await Group.findOneBy({ codeName });
if (!group) {
console.log(`No group with the code name "${codeName}" was found.`);
return;
}
user.groups.push(group);
}
try {
console.log(
await user.save()
);
} catch (error: any) {
console.log(error.message);
} finally {
await dataSource.destroy();
}
}
Then you can create a user with their permissions and groups through the command line.
npm run build
foal run create-user userPermissions="[ \"my-first-perm\" ]" groups="[ \"my-group\" ]"
Fetching a User with their Permissions
If you want the hasPerm method to work on the context user property, you must use the User.findOneWithPermissionsBy method in the authentication hook.
Example with JSON Web Tokens
import { Context, Get } from '@foal/core';
import { JWTRequired } from '@foal/jwt';
@JWTRequired({
user: (id: number) => User.findOneWithPermissionsBy({ id })
})
export class ProductController {
@Get('/products')
readProduct(ctx: Context) {
if (!ctx.user.hasPerm('read-products')) {
return new HttpResponseForbidden();
}
return new HttpResponseOK([]);
}
}
Example with Sessions Tokens
import { Context, Get, UseSessions } from '@foal/core';
@UseSessions({
required: true,
user: (id: number) => User.findOneWithPermissionsBy({ id }),
})
export class ProductController {
@Get('/products')
readProduct(ctx: Context) {
if (!ctx.user.hasPerm('read-products')) {
return new HttpResponseForbidden();
}
return new HttpResponseOK([]);
}
}
The PermissionRequired Hook
This requires the use of
User.findOneWithPermissionsBy.
import { PermissionRequired } from '@foal/core';
@PermissionRequired('perm')
| Context | Response |
|---|---|
ctx.user is null | 401 - UNAUTHORIZED |
ctx.user.hasPerm('perm') is false | 403 - FORBIDDEN |
import { PermissionRequired } from '@foal/core';
@PermissionRequired('perm', { redirect: '/login' })
| Context | Response |
|---|---|
ctx.user is null | Redirects to /login (302 - FOUND) |
ctx.user.hasPerm('perm') is false | 403 - FORBIDDEN |
Example
import { Context, Get, PermissionRequired } from '@foal/core';
import { JWTRequired } from '@foal/jwt';
@JWTRequired({ user: (id: number) => User.findOneWithPermissionsBy({ id }) })
export class ProductController {
@Get('/products')
@PermissionRequired('read-products')
readProduct(ctx: Context) {
return new HttpResponseOK([]);
}
}
BaseEntity Inheritance
The classes Permission, Group and UserWithPermissions all extends the BaseEntity class so you can access its static and instance methods.
Example
const perm = await Permission.findOneByOrFail({ codeName: 'perm1' });
perm.name = 'Permission1';
await perm.save();
Get All Users with a Given Permission
The class UserWithPermissions provides a static method withPerm to get all users with a given permission. It returns all users that have this permission on their own or through the groups they belong to.
@Entity()
class User extends UserWithPermissions {}
const users = await User.withPerm<User>('perm1');