Social Authentication
In addition to traditional password authentication, Foal provides services to authenticate users through social providers. The framework officially supports the following:
- Github
If your provider is not listed here but supports OAuth 2.0, then you can still extend the AbstractProvider class to integrate it or use a community provider below.
Get Started
General overview
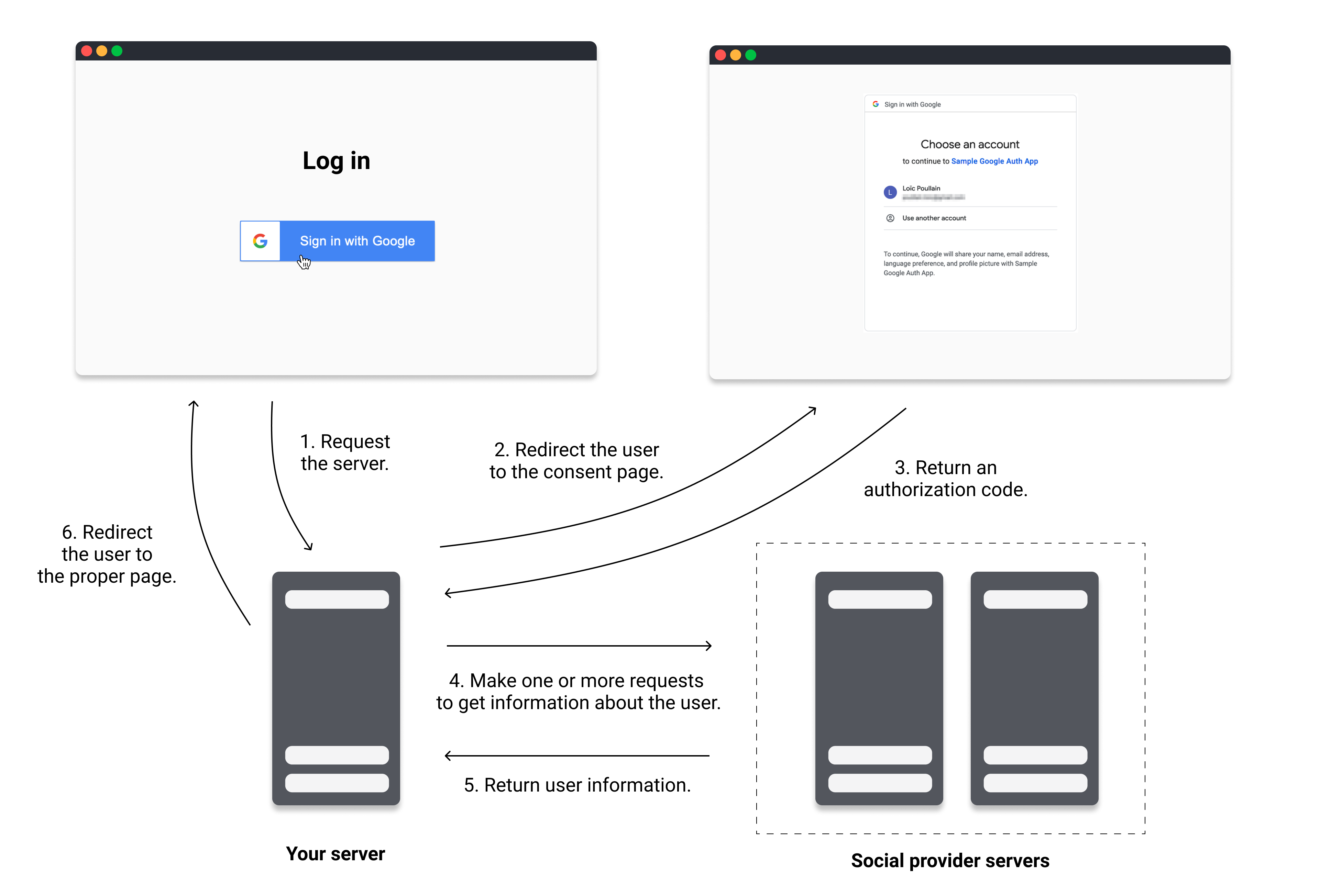
The authentication process works as follows:
- The user clicks the Log In with xxx button in the browser and the client sends a request to the server.
- The server redirects the user to the consent page where they are asked to give permission to log in with their account and/or give access to some of their personal information.
- The user approves and the consent page redirects the user with an authorization code to the redirect URI specified in the configuration.
- Your application then makes one or more requests to the OAuth servers to obtain an access token and information about the user.
- The social provider servers return this information.
- Finally, your server-side application logs the user in based on this information and redirects the user when done.
This explanation of OAuth 2 is intentionally simplified. It highlights only the parts of the protocol that are necessary to successfully implement social authentication with Foal. But the framework also performs other tasks under the hood to fully comply with the OAuth 2.0 protocol and it adds security protection against CSRF attacks.
Registering an application
To set up social authentication with Foal, you first need to register your application to the social provider you chose (Google, Facebook, etc). This can be done through its website.
Usually your are required to provide:
- an application name,
- a logo,
- and redirect URIs where the social provider should redirect the users once they give their consent on the provider page (ex:
http://localhost:3001/signin/google/callback,https://example.com/signin/google/callback).
Once done, you should receive:
- a client ID that is public and identifies your application,
- and a client secret that must not be revealed and can therefore only be used on the backend side. It is used when your server communicates with the OAuth provider's servers.
You must obtain a client secret. If you do not have one, it means you probably chose the wrong option at some point.
Installation and configuration
Once you have registered your application, install the appropriate package.
npm install @foal/social
Then, you will need to provide your client ID, client secret and your redirect URIs to Foal. This can be done through the usual configuration files.
- YAML
- JSON
- JS
settings:
social:
google:
clientId: 'xxx'
clientSecret: 'env(SETTINGS_SOCIAL_GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET)'
redirectUri: 'http://localhost:3001/signin/google/callback'
{
"settings": {
"social": {
"google": {
"clientId": "xxx",
"clientSecret": "env(SETTINGS_SOCIAL_GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET)",
"redirectUri": "http://localhost:3001/signin/google/callback"
}
}
}
}
module.exports = {
settings: {
social: {
google: {
clientId: 'xxx',
clientSecret: 'env(SETTINGS_SOCIAL_GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET)',
redirectUri: 'http://localhost:3001/signin/google/callback'
}
}
}
}
.env
SETTINGS_SOCIAL_GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET=yyy
Adding controllers
The last step is to add a controller that will call methods of a social service to handle authentication. The example below uses Google as provider.
// 3p
import { Context, dependency, Get } from '@foal/core';
import { GoogleProvider } from '@foal/social';
export class AuthController {
@dependency
google: GoogleProvider;
@Get('/signin/google')
redirectToGoogle() {
// Your "Login In with Google" button should point to this route.
// The user will be redirected to Google auth page.
return this.google.createHttpResponseWithConsentPageUrl({ isRedirection: true });
}
@Get('/signin/google/callback')
async handleGoogleRedirection(ctx: Context) {
// Once the user gives their permission to log in with Google, the OAuth server
// will redirect the user to this route. This route must match the redirect URI.
const { userInfo, tokens } = await this.google.getUserInfo(ctx);
// Do something with the user information AND/OR the access token.
// If you only need the access token, you can call the "getTokens" method.
// The method usually ends with a HttpResponseRedirect object as returned value.
}
}
You can also override in the createHttpResponseWithConsentPageUrl method the scopes you want:
return this.google.createHttpResponseWithConsentPageUrl({ isRedirection: true, scopes: [ 'email' ] });
Additional parameters can passed to the createHttpResponseWithConsentPageUrl and getUserInfo methods depending on the provider.
If you want to manage the redirection on the client side manually, don't specify the
isRedirectionoption. In this case, thecreateHttpResponseWithConsentPageUrlmethod returns anHttpResponseOKwhose body contains the URL of the consent page. The name of the body property isconsentPageUrl.
Techniques
Usage with sessions
This example shows how to manage authentication (login and registration) with sessions.
user.entity.ts
import { BaseEntity, Column, Entity, PrimaryGeneratedColumn } from 'typeorm';
@Entity()
export class User extends BaseEntity {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@Column({ unique: true })
email: string;
}
export { DatabaseSession } from '@foal/typeorm';
auth.controller.ts
// 3p
import {
Context,
dependency,
Get,
HttpResponseRedirect,
Store,
UseSessions,
} from '@foal/core';
import { GoogleProvider } from '@foal/social';
import { User } from '../entities';
export class AuthController {
@dependency
google: GoogleProvider;
@dependency
store: Store;
@Get('/signin/google')
redirectToGoogle() {
return this.google.createHttpResponseWithConsentPageUrl({ isRedirection: true });
}
@Get('/signin/google/callback')
@UseSessions({
cookie: true,
})
async handleGoogleRedirection(ctx: Context<User>) {
const { userInfo } = await this.google.getUserInfo(ctx);
if (!userInfo.email) {
throw new Error('Google should have returned an email address.');
}
let user = await User.findOneBy({ email: userInfo.email });
if (!user) {
// If the user has not already signed up, then add them to the database.
user = new User();
user.email = userInfo.email;
await user.save();
}
ctx.session!.setUser(user);
return new HttpResponseRedirect('/');
}
}
Usage with JWT
This example shows how to manage authentication (login and registration) with JWT.
user.entity.ts
import { BaseEntity, Column, Entity, PrimaryGeneratedColumn } from 'typeorm';
@Entity()
export class User extends BaseEntity {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@Column({ unique: true })
email: string;
}
auth.controller.ts
// std
import { promisify } from 'util';
// 3p
import {
Context,
dependency,
Get,
HttpResponseRedirect,
} from '@foal/core';
import { GoogleProvider } from '@foal/social';
import { getSecretOrPrivateKey, setAuthCookie } from '@foal/jwt';
import { sign } from 'jsonwebtoken';
import { User } from '../entities';
export class AuthController {
@dependency
google: GoogleProvider;
@Get('/signin/google')
redirectToGoogle() {
return this.google.createHttpResponseWithConsentPageUrl({ isRedirection: true });
}
@Get('/signin/google/callback')
async handleGoogleRedirection(ctx: Context) {
const { userInfo } = await this.google.getUserInfo(ctx);
if (!userInfo.email) {
throw new Error('Google should have returned an email address.');
}
let user = await User.findOneBy({ email: userInfo.email });
if (!user) {
// If the user has not already signed up, then add them to the database.
user = new User();
user.email = userInfo.email;
await user.save();
}
const payload = {
email: user.email,
id: user.id,
};
const jwt = await promisify(sign as any)(
payload,
getSecretOrPrivateKey(),
{ subject: user.id.toString() }
);
const response = new HttpResponseRedirect('/');
await setAuthCookie(response, jwt);
return response;
}
}
Custom Provider
If your provider is not officially supported by Foal but supports the OAuth 2.0 protocol, you can still implement your own social service. All you need to do is to make it inherit from the AbstractProvider class.
Example
// 3p
import { AbstractProvider, SocialTokens } from '@foal/core';
export interface GithubAuthParameter {
// ...
}
export interface GithubUserInfoParameter {
// ...
}
export interface GithubUserInfo {
// ...
}
export class GithubProvider extends AbstractProvider<GithubAuthParameter, GithubUserInfoParameter, GithubUserInfo> {
protected configPaths = {
clientId: 'social.github.clientId',
clientSecret: 'social.github.clientSecret',
redirectUri: 'social.github.redirectUri',
};
protected authEndpoint = '...';
protected tokenEndpoint = '...';
protected userInfoEndpoint = '...'; // Optional. Depending on the provider.
protected defaultScopes: string[] = [ 'email' ]; // Optional
getUserInfoFromTokens(tokens: SocialTokens, params?: GithubUserInfoParameter): GithubUserInfo | Promise<GithubUserInfo> {
// ...
// In case the server returns an error when requesting
// user information, you can throw a UserInfoError.
}
}
Sending the Client Credentials in an Authorization Header
When requesting the token endpoint, the provider sends the client ID and secret as a query parameter by default. If you want to send them in an Authorization header using the basic scheme, you can do so by setting the useAuthorizationHeaderForTokenEndpoint property to true.
Enabling Code Flow with PKCE
If you want to enable code flow with PKCE, you can do so by setting the usePKCE property to true.
By default, the provider will perform a SHA256 hash to generate the code challenge. If you wish to use the plaintext code verifier string as code challenge, you can do so by setting the
useCodeVerifierAsCodeChallengeproperty totrue.
When using this feature, the provider encrypts the code verifier and stores it in a cookie on the client. In order to do this, you need to provide a secret using the configuration key settings.social.secret.codeVerifierSecret.
- YAML
- JSON
- JS
settings:
social:
secret:
codeVerifierSecret: 'xxx'
{
"settings": {
"social": {
"secret": {
"codeVerifierSecret": "xxx"
}
}
}
}
module.exports = {
settings: {
social: {
secret: {
codeVerifierSecret: 'xxx'
}
}
}
}
Official Providers
Google
| Service name | Default scopes | Available scopes |
|---|---|---|
GoogleProvider | openid, profile, email | Google scopes |
Register an OAuth application
Visit the Google API Console to obtain a client ID and a client secret.
Redirection parameters
The createHttpResponseWithConsentPageUrl method of the GoogleProvider accepts additional parameters. These parameters and their description are listed here and are all optional.
Example
this.google.createHttpResponseWithConsentPageUrl({ /* ... */ }, {
access_type: 'offline'
})
Facebook
| Service name | Default scopes | Available scopes |
|---|---|---|
FacebookProvider | email | Facebook permissions |
Register an OAuth application
Visit Facebook's developer website to create an application and obtain a client ID and a client secret.
Redirection parameters
The createHttpResponseWithConsentPageUrl method of the FacebookProvider accepts an additional auth_type parameter which is optional.
Example
this.facebook.createHttpResponseWithConsentPageUrl({ /* ... */ }, {
auth_type: 'rerequest'
});
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
auth_type | 'rerequest' | If a user has already declined a permission, the Facebook Login Dialog box will no longer ask for this permission. The auth_type parameter explicity tells Facebook to ask the user again for the denied permission. |
User info parameters
The getUserInfo and getUserInfoFromTokens methods of the FacebookProvider accept an additional fields parameter which is optional.
Example
const { userInfo } = await this.facebook.getUserInfo(ctx, {
fields: [ 'email' ]
})
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
fields | string[] | List of fields that the returned user info object should contain. These fields may or may not be available depending on the permissions (scopes) that were requested with the createHttpResponseWithConsentPageUrl method. Default: ['id', 'name', 'email']. |
Github
| Service name | Default scopes | Available scopes |
|---|---|---|
GithubProvider | none | Github scopes |
Register an OAuth application
Visit this page to create an application and obtain a client ID and a client secret.
Additional documentation on Github's redirect URLs can be found here.
Redirection parameters
The createHttpResponseWithConsentPageUrl method of the GithubProvider accepts additional parameters. These parameters and their description are listed below and are all optional.
Example
this.github.createHttpResponseWithConsentPageUrl({ /* ... */ }, {
allow_signup: false
})
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
login | string | Suggests a specific account to use for signing in and authorizing the app. |
allow_signup | boolean | Whether or not unauthenticated users will be offered an option to sign up for GitHub during the OAuth flow. The default is true. Use false in the case that a policy prohibits signups. |
Source: https://developer.github.com/apps/building-oauth-apps/authorizing-oauth-apps/#parameters
LinkedIn
| Service name | Default scopes | Available scopes |
|---|---|---|
LinkedInProvider | r_liteprofile | API documentation |
Register an OAuth application
Visit this page to create an application and obtain a client ID and a client secret.
User info parameters
The getUserInfo and getUserInfoFromTokens methods of the LinkedInProvider accept an additional projection parameter which is optional.
Example
const { userInfo } = await this.linkedin.getUserInfo(ctx, {
fields: [ 'id', 'firstName' ]
})
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
fields | string[] | List of fields that the returned user info object should contain. Additional documentation on field projections. |
projection | string | LinkedIn projection parameter. |
Twitter
| Service name | Default scopes | Available scopes |
|---|---|---|
TwitterProvider | users.read tweet.read | API documentation |
Register an OAuth application
Visit this page to create an application and obtain a client ID and a client secret. You must configure Oauth2 settings to be used with public client;
Community Providers
There are no community providers available yet! If you want to share one, feel free to open a PR on Github.
Common Errors
| Error | Description |
|---|---|
InvalidStateError | The state query does not match the value found in the cookie. |
CodeVerifierNotFound | The encrypted code verifier was not found in the cookie (only when using PKCE). |
AuthorizationError | The authorization server returns an error. This can happen when a user does not give consent on the provider page. |
UserInfoError | Thrown in AbstractProvider.getUserFromTokens if the request to the resource server is unsuccessful. |
Security
HTTPS
When deploying the application, you application must use HTTPS.
production.yml
settings:
social:
cookie:
# Only pass the state cookie if the request is transmitted over a secure channel (HTTPS).
secure: true
google:
# Your redirect URI in production
redirectUri: 'https://example.com/signin/google/callback'